Cyberattacks are any ill attempts to access systems, networks, or data without the right to access it with the aim of stealing information, disrupting operation or damaging money. Cyberattacks in the modern hyper-connected world grow at a pace because of the digital transformation and remote working, use of clouds, and the advancement of sophisticated hackers.
Since phishing mails to extortion software, cybercriminals are continually advancing their methods, and cybersecurity is a major issue to everybody. No one can claim to be totally safe especially with more personal and business data being stored online than ever before.
Cybersecurity threats are unique to individuals, businesses of any size, and remote workers, and therefore, it is important to understand and mitigate cyber threats.
Who Is at Risk of Cyberattacks?
| Target Group |
Why They Are at Risk |
Common Threats Faced |
| Individuals |
Weak passwords, lack of security awareness |
Phishing, identity theft, malware |
| Small Businesses |
Limited cybersecurity budgets and expertise |
Ransomware, data breaches, email scams |
| Large Enterprises |
Large volumes of valuable data |
Advanced persistent threats, insider attacks |
| Remote Workers |
Use of public Wi-Fi and personal devices |
Man-in-the-middle attacks, credential theft |
| Online Shoppers |
Frequent online transactions |
Payment fraud, fake websites |
| Students |
Use of shared or unsecured networks |
Account hijacking, spyware |
Importance of Proactive Cybersecurity Habits
| Cybersecurity Habit |
Why It Matters |
Potential Benefit |
| Regular Software Updates |
Fixes known vulnerabilities |
Reduces exposure to exploits |
| Strong Password Practices |
Prevents unauthorized account access |
Protects personal and business data |
| Multi-Factor Authentication |
Adds an extra layer of security |
Stops most credential-based attacks |
| Email Awareness |
Helps identify phishing and scam attempts |
Prevents data theft and malware infections |
| Data Backups |
Ensures recovery after attacks |
Minimizes data loss and downtime |
| Continuous Security Learning |
Keeps users aware of evolving threats |
Improves long-term cyber resilience |
Understand Common Types of Cyberattacks
| Type of Cyberattack |
What It Is |
How It Works |
Potential Impact |
| Phishing Attacks |
Fraudulent messages designed to steal sensitive information |
Attackers send fake emails or messages posing as trusted sources |
Account compromise, financial loss, identity theft |
| Spear-Phishing Attacks |
Targeted version of phishing aimed at specific individuals or organizations |
Uses personal or work-related details to appear legitimate |
Data breaches, corporate espionage, ransomware delivery |
| Malware |
Malicious software created to damage or disrupt systems |
Installed through infected files, links, or downloads |
System damage, data theft, performance issues |
| Ransomware |
A type of malware that encrypts data and demands payment |
Locks files until a ransom is paid |
Data loss, business downtime, financial damage |
| Spyware |
Malware that secretly monitors user activity |
Collects keystrokes, passwords, and browsing data |
Privacy invasion, credential theft |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks |
Interception of communication between two parties |
Often occurs on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks |
Data interception, session hijacking |
| Password Attacks |
Attempts to gain access using stolen or guessed passwords |
Includes brute force and credential-stuffing methods |
Unauthorized access, account takeovers |
| Credential-Stuffing Attacks |
Automated login attempts using leaked credentials |
Reuses stolen username-password combinations |
Large-scale account breaches |
| Social Engineering Scams |
Psychological manipulation to trick users |
Exploits trust, fear, or urgency |
Data theft, financial fraud, malware infection |
Use Strong and Unique Passwords
| Password Best Practice |
Explanation |
Why It Matters |
| Characteristics of a Strong Password |
Uses at least 12–16 characters with a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols |
Makes passwords harder to guess or crack |
| Avoid Password Reuse |
Using the same password across multiple accounts |
A single breach can expose all linked accounts |
| Use Password Managers |
Secure tools that generate and store complex passwords |
Eliminates the need to remember multiple passwords |
| Regular Password Updates |
Changing passwords periodically or after a breach |
Reduces long-term exposure to compromised credentials |
| Unique Passwords Per Account |
Each account has a different password |
Limits damage if one account is hacked |
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
| MFA Aspect |
Description |
Security Benefit |
| What MFA Is |
A security method requiring two or more verification steps |
Adds an extra barrier beyond passwords |
| How MFA Works |
Combines something you know (password) with something you have or are |
Prevents unauthorized access even if passwords are stolen |
| SMS-Based MFA |
One-time codes sent via text message |
Better than passwords alone, but less secure |
| Authenticator Apps |
Time-based codes generated by mobile apps |
Stronger protection than SMS |
| Biometric MFA |
Fingerprint, face, or retina recognition |
Highly secure and convenient |
| Critical Accounts for MFA |
Email, banking, cloud storage, admin dashboards |
Protects high-value and sensitive data |
Keep Software and Systems Updated
| Update Aspect |
Explanation |
Security Benefit |
| Outdated Software Risks |
Old software contains known vulnerabilities exploited by attackers |
Increases exposure to malware and hacking |
| OS, Browser & App Updates |
Updates fix bugs and security loopholes across systems |
Improves overall device protection |
| Automatic Updates |
Updates install automatically without user action |
Ensures timely protection with minimal effort |
| Manual Updates |
Users choose when and what to update |
Useful for controlled environments but risk delays |
| Patching Vulnerabilities on Time |
Applying security patches as soon as released |
Prevents exploitation of known weaknesses |
Be Cautious with Emails and Links
| Email Safety Measure |
What to Look For |
Why It Matters |
| Identifying Phishing Emails |
Urgent language, fake branding, spelling errors |
Helps avoid credential theft |
| Suspicious Links |
Mismatched URLs, shortened links, strange domains |
Prevents redirection to malicious sites |
| Dangerous Attachments |
Unexpected files or executable attachments |
Reduces malware infections |
| Safe Email Practices |
Don’t click unknown links, use spam filters |
Minimizes attack surface |
| Verifying Senders |
Check email addresses and domain names carefully |
Confirms legitimacy before interaction |
| Work vs Personal Email Use |
Avoid mixing work credentials with personal emails |
Protects corporate and personal data |
Secure Your Internet Connection
| Internet Security Practice |
Description |
Security Advantage |
| Using Secure Wi-Fi Networks |
Connect only to password-protected and encrypted networks |
Prevents unauthorized access |
| Risks of Public Wi-Fi |
Open networks allow attackers to intercept data |
Increases risk of data theft |
| VPN Usage |
Encrypts internet traffic and hides IP address |
Protects privacy on public and private networks |
| VPN Benefits |
Secures remote work and browsing activity |
Prevents tracking and MITM attacks |
| Router Security Best Practices |
Change default passwords, enable WPA3, update firmware |
Strengthens home and office network security |
Install and Maintain Security Software
| Security Software Component |
Purpose |
Why It’s Important |
| Antivirus Software |
Detects and removes malicious files |
Protects against common malware |
| Anti-Malware Tools |
Identifies advanced and zero-day threats |
Adds an extra layer of defense |
| Firewalls (Personal) |
Monitors incoming and outgoing traffic |
Blocks unauthorized access |
| Firewalls (Network-Level) |
Protects entire networks and devices |
Essential for businesses |
| Real-Time Protection |
Continuously scans activity |
Stops threats before damage occurs |
| Regular Security Scans |
Checks systems for hidden threats |
Ensures ongoing system health |
| Choosing Reputable Software |
Select trusted, regularly updated tools |
Reduces false security risks |
Protect Personal and Sensitive Data
| Data Protection Practice |
Explanation |
Security Benefit |
| Limiting Data Sharing Online |
Avoid oversharing personal details on websites and social media |
Reduces identity theft risk |
| Encrypting Files and Devices |
Converts data into unreadable formats without authorization |
Protects data even if devices are stolen |
| Secure Cloud Storage |
Uses encryption, strong access controls, and MFA |
Keeps files safe from unauthorized access |
| Handling Financial Information Safely |
Protects card numbers, banking details, and payment credentials |
Prevents financial fraud |
| Protecting Login Credentials |
Never share passwords or store them in plain text |
Reduces account compromise |
Educate Yourself and Your Team
| Awareness Area |
Description |
Why It Matters |
| Cybersecurity Awareness |
Understanding modern cyber threats |
Reduces human-based security risks |
| Human-Error Vulnerabilities |
Mistakes like clicking malicious links or weak passwords |
Major cause of cyber breaches |
| Employee Training Programs |
Regular training on security policies and threats |
Strengthens organizational defense |
| Security Policies |
Clear guidelines for data and system usage |
Ensures consistent protection |
| Staying Updated on Threats |
Tracking new attack methods and trends |
Improves preparedness |
Backup Your Data Regularly
| Backup Strategy |
Purpose |
Benefit |
| Importance of Backups |
Enables recovery after ransomware attacks |
Prevents permanent data loss |
| Cloud Backups |
Stores data off-site |
Protects against physical damage |
| Local Backups |
Saves data on external drives |
Fast recovery access |
| Hybrid Backups |
Combines cloud and local storage |
Maximum reliability |
| Backup Frequency |
Daily or weekly backups |
Minimizes data loss |
| Testing Backups |
Ensures backups can be restored |
Confirms data integrity |
Monitor Accounts and Devices
| Monitoring Action |
What to Watch For |
Response Benefit |
| Signs of Cyberattacks |
Unusual logins, slow systems, unknown files |
Early detection of threats |
| Login Activity Monitoring |
Reviewing account access history |
Identifies unauthorized access |
| Security Alerts |
Notifications of suspicious activity |
Enables quick response |
| Suspected Breach Response |
Change passwords, disconnect devices |
Limits further damage |
| Incident Reporting |
Notify IT or service providers immediately |
Speeds up containment |
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks on Businesses
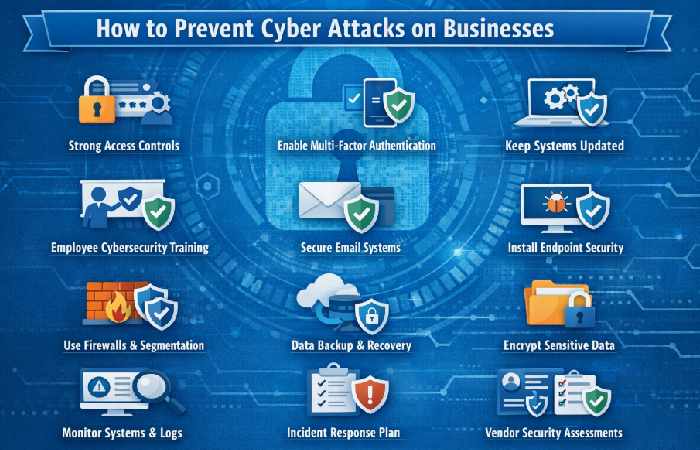
| Prevention Strategy |
What Businesses Should Do |
Security Benefit |
| Implement Strong Access Controls |
Use strong passwords, role-based access, and least-privilege policies |
Limits unauthorized system access |
| Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) |
Apply MFA to email, cloud apps, VPNs, and admin accounts |
Stops most credential-based attacks |
| Keep Systems & Software Updated |
Regularly patch OS, servers, and business applications |
Closes known security vulnerabilities |
| Employee Cybersecurity Training |
Train staff to recognize phishing and social engineering |
Reduces human-error breaches |
| Secure Business Email Systems |
Use spam filters, DMARC, SPF, and DKIM |
Prevents email spoofing and phishing |
| Install Endpoint Security Software |
Deploy antivirus, anti-malware, and EDR tools |
Detects and blocks malicious activity |
| Use Firewalls & Network Segmentation |
Separate critical systems from general networks |
Contains breaches and limits damage |
| Secure Remote Work Environments |
Use VPNs, secured Wi-Fi, and device policies |
Protects remote employees |
| Regular Data Backups |
Maintain encrypted, offline, or cloud backups |
Ensures recovery from ransomware |
| Encrypt Sensitive Business Data |
Encrypt files, databases, and devices |
Protects data even if systems are breached |
| Monitor Systems & Logs |
Track unusual activity and access attempts |
Enables early threat detection |
| Incident Response Plan |
Prepare steps for handling cyber incidents |
Reduces downtime and financial loss |
| Vendor & Third-Party Risk Management |
Assess security practices of partners |
Prevents supply-chain attacks |
| Conduct Security Audits |
Perform vulnerability scans and penetration tests |
Identifies weak points before attackers do |
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks at Home
| Prevention Step |
What to Do at Home |
Security Benefit |
| Use Strong, Unique Passwords |
Create long passwords and avoid reuse across accounts |
Prevents account takeovers |
| Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) |
Turn on 2FA for email, banking, and social media |
Adds an extra security layer |
| Secure Your Home Wi-Fi |
Change router defaults, use WPA3/WPA2 encryption |
Blocks unauthorized access |
| Keep Devices Updated |
Update phones, computers, routers, and smart devices |
Fixes security vulnerabilities |
| Install Antivirus & Firewall |
Use trusted security software on all devices |
Detects and blocks malware |
| Be Careful with Emails & Links |
Avoid clicking unknown links or attachments |
Prevents phishing and scams |
| Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Tasks |
Don’t access banking on open networks |
Reduces data interception risk |
| Use a VPN When Needed |
Encrypt internet traffic on shared networks |
Protects privacy |
| Limit Personal Information Online |
Share minimal details on social media |
Reduces identity theft risk |
| Back Up Important Data |
Use cloud or external drive backups |
Protects against ransomware |
| Monitor Account Activity |
Check login alerts and unusual behavior |
Detects attacks early |
| Educate Family Members |
Teach kids and elders basic cyber safety |
Reduces human-error attacks |
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is not a single-time operation, but an ongoing process which needs awareness, consistency and taking initiative. With the continuous development of cyber threats, such minor steps as a strong password, frequent updates, data backups can lead to a huge difference.
Related Reading: Check out our guide on how to choose the right Android Apps for Small Business 2025


